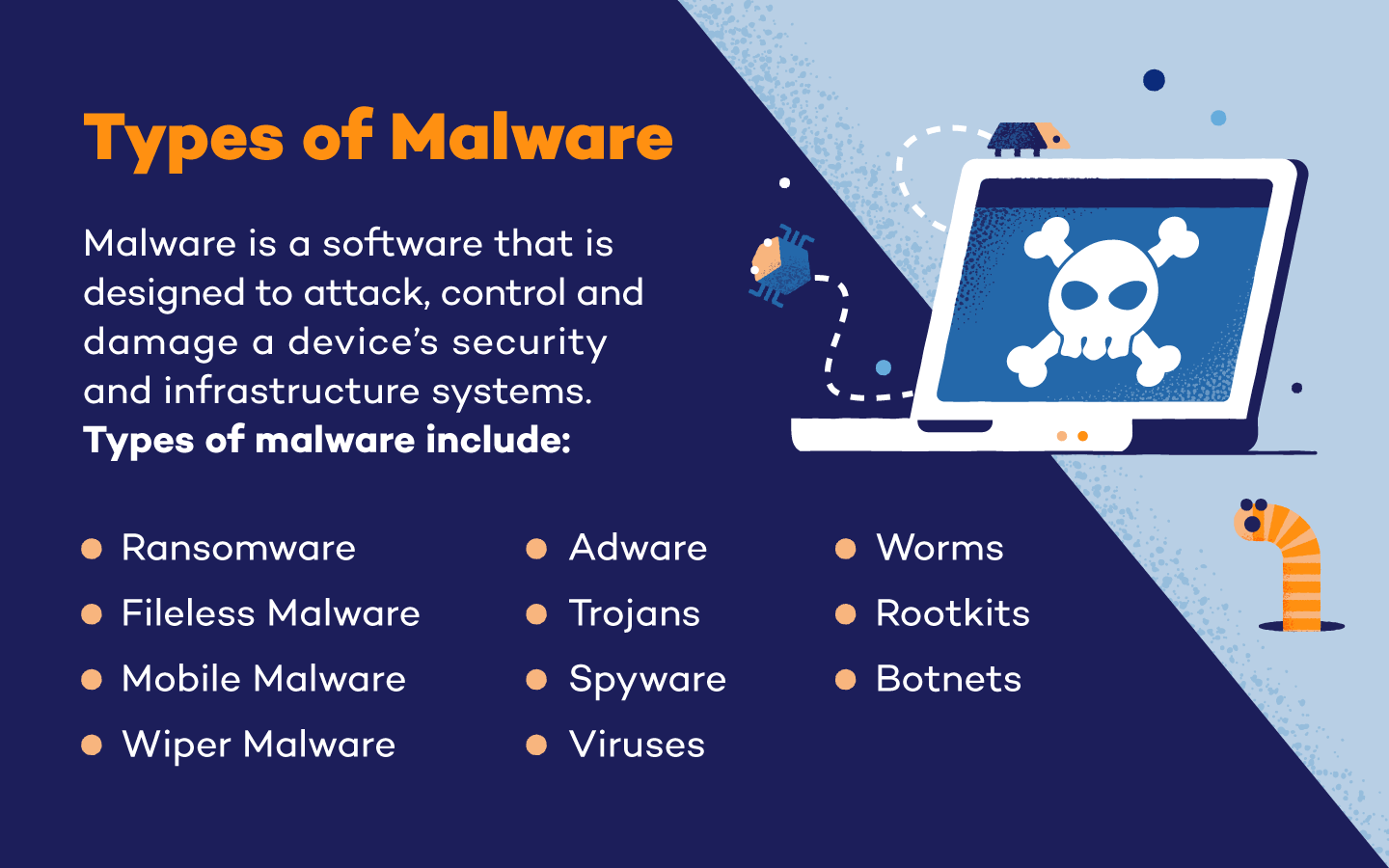
Common Types of Malware
While there are a variety of malware types and sub-types, there are 11 specific types of malware that are considered the most common. These types of malware include:
1. Ransomware
Ransomware is a virus that encrypts all the files on an infected device. Once encrypted, the device becomes unusable because none of the data stored on it can be accessed.
Ransomware attacks will request a ransome in exchange for a decryption key that will unlock a device’s files. As there is no guarantee that the hacker will release the decryption key, paying a ransom is not an ideal solution. To prevent ransomware attacks, keep a current backup of all your files on hand so you can restore you device yourself.
Types of Ransomware:
Rogue Security Software: Rogue security software is a type of ransomware that poses as a virus or security breach. Users are required to pay the rogue software to remove the fake issue.
Crypto-malware: Ransomwares that request ransoms in cryptocurrency are frequently referred to as crypto-malware.
2. Fileless Malware
Fileless malware is a type of malware that uses macros and system tools to invade a system rather than executable files. This type of malware will edit already installed files, which many systems recognize as legitimate. Fileless malware is difficult to protect against because there is no malicious program installed.
To protect your devices against fileless malware, limit login credentials and knowledge. Multifactor authentication is also an additional protective element that can keep hackers from infiltrating a system and running stealth operations unknowingly.
3. Adware
Adware does exactly what the name suggests — tracks internet surfing habits and suggests ads and spam to the user. While this type of malware doesn’t install anything onto your device, it can hamper performance which can make your items more vulnerable to other types of attacks.
Adware that plants malicious ads onto a users device is known as malvertising. These types of malware are intended to plant dangerous code onto a device when a link, pop-up or advertisment is clicked on. Updated operating systems and spam filters can help protect devices against adware.
4. Trojans
Trojans, named after the Greek legend of the Trojan Horse, are a type of malware that sneaks onto a victim’s device. Once installed, the trojan waits to be activated before attacking.
This form of malware may delete and damage data or simply create a backdoor, allowing hackers to access and use the infected device when they choose. Trojans are a popular way to connect devices to botnets — another type of malware — or launch distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS).
5. Spyware
Modern systems are designed to protect passwords and sensitive data using encryption. Spyware helps attackers get around and break down encrypted data.
Once installed, spyware collects and logs usage data — including the websites you visit, credentials you use and keyboard buttons you push. This information is periodically updated, reported and reassembled, allowing the hacker to read your passwords and use them to break into your online accounts.
Types of spyware:
Keyloggers: Keyloggers are a type of spyware that monitors the keystrokes on your keyboard. These can be used to steal password data, bank information and more.
Grayware: While not a form of malware itself, grayware can affect the performance of a device as well as monitor its user’s behaviors and history.
RAM scrapers: RAM scrapers steal and store data from devices before it can be encrypted. For example, point-of-sale devices temporarily store credit card information, which can be monitored and stolen by RAM scrapers.
6. Viruses
Viruses may be one of the most commonly known types of malware. These invaders can affect device speed and performance, steal sensitive data, damage and destroy files and create backdoor opportunities for larger scale attacks.
Viruses depend on host applications to run and survive. Removing a virus requires users to also remove its host. Additionally, viruses can infect additional systems, and downloading antivirus software is the best way to prevent this type of malware from affecting your devices.
Type of Virus:
Logic bombs: Logic bombs will only attack a system once they have been triggered. These triggers can be a certain date and time, a specific number of logins or the startup of a certain application. These are used by viruses to deliver malicious code at specified times, and they can go completely undetected until triggered.
7. Worms
A worm is a type of virus designed to copy itself and spread to devices on a shared network. This means that an infection on your home PC can quickly spread to your laptop, phone and any other systems connected to the same network.
While the infection may not necessarily damage or delete files, it can cause your devices and network to slow down or become unresponsive. This type of malware may also use your digital address book to email itself to other people you know, potentially infecting their devices, too.
8. Rootkits
Injected into applications and firmware, rootkits are a type of malware that give hackers complete remote control of an infected device. Because this software gives attackers administrative privileges, they can conceal other malware attacks and affect different types of files.
Rootkits were not initially created as malware, but their remote capabilities have made them a favorite attack option of hackers. Multiauthentication and limited administrative credentials can help protect against this malware type.
9. Botnets
A botnet, made up of bots, is a software that is able to follow automated, remote commands. While many botnets and bots are used for important, legitimate tasks — like search engine indexing — they can also be used as a type of malware that attacks central servers.
If botnets are used for flood attacks like DDoS attacks, they can incapacitate systems, servers and devices. Additionally, botnets can include large numbers of technological devices, so they can be difficult to shut down completely.
10. Mobile Malware
Unlike traditional types of malware, mobile malware is designed to target a specific type of device: mobile devices. Mobile malware for smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices can spy on user actions, steal credentials, overtake administrative privileges and more.
Mobile malware is frequently spread through SMS phishing (smishing) and text message scams. Trojans, ransomware and adware targeting mobile devices can also be considered mobile malware. Additionally, jailbroken phones are at a higher risk of a mobile malware invasion.
11. Wiper Malware
Wiper malware is a type of malware with the sole purpose of erasing data and making it unrecoverable. Many attackers who use wiper malware use this type of attack to target both private and public businesses.
Wiper malware is also used after other malware attacks. Because it can erase and destroy data, attackers will use wipler malware to remove traces of invasions, which can make organizational recovery difficult to impossible.
Common Types of Malware
While there are a variety of malware types and sub-types, there are 11 specific types of malware that are considered the most common. These types of malware include:
1. Ransomware
Ransomware is a virus that encrypts all the files on an infected device. Once encrypted, the device becomes unusable because none of the data stored on it can be accessed.
Ransomware attacks will request a ransome in exchange for a decryption key that will unlock a device’s files. As there is no guarantee that the hacker will release the decryption key, paying a ransom is not an ideal solution. To prevent ransomware attacks, keep a current backup of all your files on hand so you can restore you device yourself.
Types of Ransomware:
Rogue Security Software: Rogue security software is a type of ransomware that poses as a virus or security breach. Users are required to pay the rogue software to remove the fake issue.
Crypto-malware: Ransomwares that request ransoms in cryptocurrency are frequently referred to as crypto-malware.
2. Fileless Malware
Fileless malware is a type of malware that uses macros and system tools to invade a system rather than executable files. This type of malware will edit already installed files, which many systems recognize as legitimate. Fileless malware is difficult to protect against because there is no malicious program installed.
To protect your devices against fileless malware, limit login credentials and knowledge. Multifactor authentication is also an additional protective element that can keep hackers from infiltrating a system and running stealth operations unknowingly.
3. Adware
Adware does exactly what the name suggests — tracks internet surfing habits and suggests ads and spam to the user. While this type of malware doesn’t install anything onto your device, it can hamper performance which can make your items more vulnerable to other types of attacks.
Adware that plants malicious ads onto a users device is known as malvertising. These types of malware are intended to plant dangerous code onto a device when a link, pop-up or advertisment is clicked on. Updated operating systems and spam filters can help protect devices against adware.
4. Trojans
Trojans, named after the Greek legend of the Trojan Horse, are a type of malware that sneaks onto a victim’s device. Once installed, the trojan waits to be activated before attacking.
This form of malware may delete and damage data or simply create a backdoor, allowing hackers to access and use the infected device when they choose. Trojans are a popular way to connect devices to botnets — another type of malware — or launch distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS).
5. Spyware
Modern systems are designed to protect passwords and sensitive data using encryption. Spyware helps attackers get around and break down encrypted data.
Once installed, spyware collects and logs usage data — including the websites you visit, credentials you use and keyboard buttons you push. This information is periodically updated, reported and reassembled, allowing the hacker to read your passwords and use them to break into your online accounts.
Types of spyware:
Keyloggers: Keyloggers are a type of spyware that monitors the keystrokes on your keyboard. These can be used to steal password data, bank information and more.
Grayware: While not a form of malware itself, grayware can affect the performance of a device as well as monitor its user’s behaviors and history.
RAM scrapers: RAM scrapers steal and store data from devices before it can be encrypted. For example, point-of-sale devices temporarily store credit card information, which can be monitored and stolen by RAM scrapers.
6. Viruses
Viruses may be one of the most commonly known types of malware. These invaders can affect device speed and performance, steal sensitive data, damage and destroy files and create backdoor opportunities for larger scale attacks.
Viruses depend on host applications to run and survive. Removing a virus requires users to also remove its host. Additionally, viruses can infect additional systems, and downloading antivirus software is the best way to prevent this type of malware from affecting your devices.
Type of Virus:
Logic bombs: Logic bombs will only attack a system once they have been triggered. These triggers can be a certain date and time, a specific number of logins or the startup of a certain application. These are used by viruses to deliver malicious code at specified times, and they can go completely undetected until triggered.
7. Worms
A worm is a type of virus designed to copy itself and spread to devices on a shared network. This means that an infection on your home PC can quickly spread to your laptop, phone and any other systems connected to the same network.
While the infection may not necessarily damage or delete files, it can cause your devices and network to slow down or become unresponsive. This type of malware may also use your digital address book to email itself to other people you know, potentially infecting their devices, too.
8. Rootkits
Injected into applications and firmware, rootkits are a type of malware that give hackers complete remote control of an infected device. Because this software gives attackers administrative privileges, they can conceal other malware attacks and affect different types of files.
Rootkits were not initially created as malware, but their remote capabilities have made them a favorite attack option of hackers. Multiauthentication and limited administrative credentials can help protect against this malware type.
9. Botnets
A botnet, made up of bots, is a software that is able to follow automated, remote commands. While many botnets and bots are used for important, legitimate tasks — like search engine indexing — they can also be used as a type of malware that attacks central servers.
If botnets are used for flood attacks like DDoS attacks, they can incapacitate systems, servers and devices. Additionally, botnets can include large numbers of technological devices, so they can be difficult to shut down completely.
10. Mobile Malware
Unlike traditional types of malware, mobile malware is designed to target a specific type of device: mobile devices. Mobile malware for smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices can spy on user actions, steal credentials, overtake administrative privileges and more.
Mobile malware is frequently spread through SMS phishing (smishing) and text message scams. Trojans, ransomware and adware targeting mobile devices can also be considered mobile malware. Additionally, jailbroken phones are at a higher risk of a mobile malware invasion.
11. Wiper Malware
Wiper malware is a type of malware with the sole purpose of erasing data and making it unrecoverable. Many attackers who use wiper malware use this type of attack to target both private and public businesses.
Wiper malware is also used after other malware attacks. Because it can erase and destroy data, attackers will use wipler malware to remove traces of invasions, which can make organizational recovery difficult to impossible.