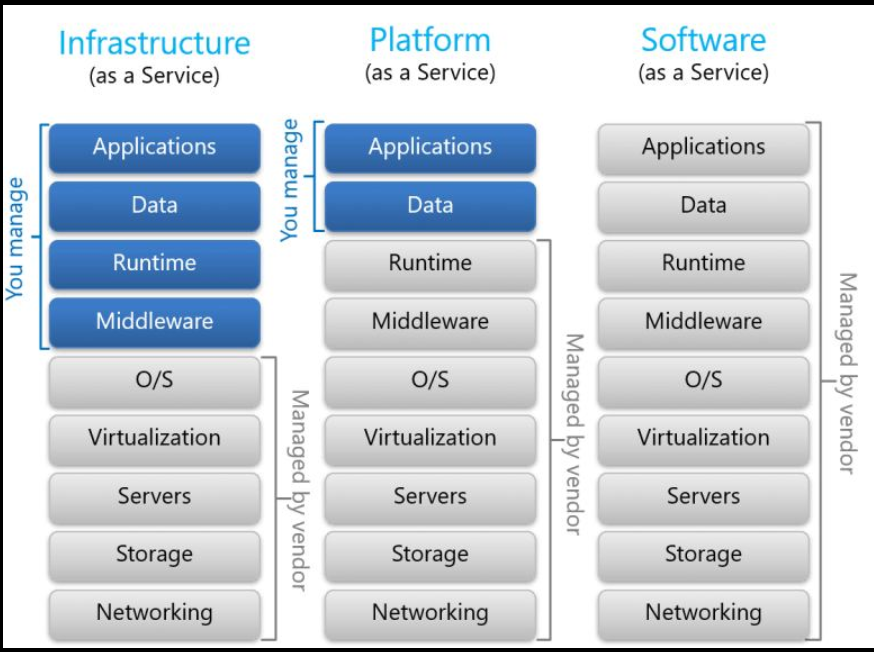
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is the most flexible category of cloud services, as it provides you with the maximum amount of control for your cloud resources. In an IaaS model, the cloud provider is responsible for maintaining the hardware, network connectivity (to the internet), and physical security. You’re responsible for everything else: operating system installation, configuration, and maintenance; network configuration; database and storage configuration; and so on. With IaaS, you’re essentially renting the hardware in a cloud data centre, but what you do with that hardware is up to you.
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a middle ground between renting space in a data centre (infrastructure as a service) and paying for a complete and deployed solution (software as a service). In a PaaS environment, the cloud provider maintains the physical infrastructure, physical security, and connection to the internet. They also maintain the operating systems, middleware, development tools, and business intelligence services that make up a cloud solution. In a PaaS scenario, you don't have to worry about the licensing or patching for operating systems and databases.
PaaS is well suited to provide a complete development environment without the headache of maintaining all the development infrastructure.
Software as a service (SaaS) is the most complete cloud service model from a product perspective. With SaaS, you’re essentially renting or using a fully developed application. Email, financial software, messaging applications, and connectivity software are all common examples of a SaaS implementation.
While the SaaS model may be the least flexible, it’s also the easiest to get up and running. It requires the least amount of technical knowledge or expertise to fully employ.